| CAAP Research Project |
Abstract
On 2000-2001 a report of the Consortium for Student Retention Data Exchange determined that retention and graduation rates in higher education institutions are consistently lower for underrepresented minorities. On 1997 a National Study of Student Support Services, conducted by the US Department of Education established that Support Services Program have a positive and statistically significant impact upon students grades, credits earned, and college retention. This paper analyzes three years of data from the College Academic Achievement Program at Michigan State University to determine its effectiveness in terms of student performance. For the purpose of this project, performance is measured in terms of the cumulative GPA achieved during the first semester of the freshman year.
Introduction
In 1971 the US Department of Education established the TRIO Programs to
help underrepresented students achieve educational goals above the secondary
level. The Federal TRIO Programs are educational opportunity outreach
programs designed to motivate and support students from disadvantaged
backgrounds. TRIO includes six outreach and support programs targeted
to serve and assist low-income, first-generation college, and disabled
students to progress through the academic pipeline from middle school
to postbaccalaureate programs.
The six programs are:
• Upward Bound
• Talent Search
• Student Support Services
• Educational Opportunity Centers
• Ronald E. McNair Postbaccalaureate Achievement
• Training Program for Federal TRIO Programs
For the last 30 years one of the TRIO Programs that has
received a significant impact in budget increase is the Student Support
Services Program. The SSS has report an increase from $10 millions in
1971 to $245 millions for the fiscal year 2001, an increase of almost
2500% in thirty years. This program has a direct impact in almost 200
thousand students nationwide.
For the Fiscal Year 2001 TRIO disbursed $730 millions in the following
programs:
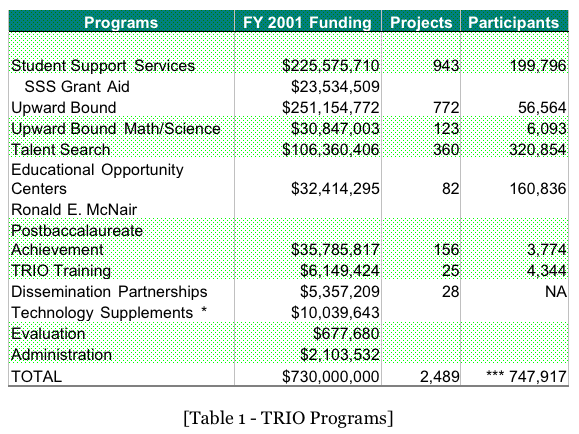
Student Support Services
The DE Student Support Services Program (SSS) focuses on improving college
retention and graduation rates of disadvantaged college students. It provides
participants with a range of academic and non-academic supplemental services,
that include tutoring, academic, career and personal counseling, remedial
assistance, and cultural enrichment activities.
According to the National Study of Student Support Services (NSSSS) conducted by the DE in 1997 participants of the program receive one or more of the following services:
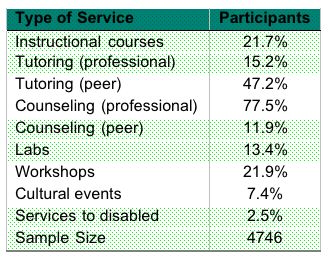
As it was found by the cited study and other research
(Massy, 2001) Support Services Program have a positive and statistically
significant impact upon students’ grades, credits earned, and college
retention. At Michigan State University the SSS Program support the College
Achievement Admissions Program, which goal is to bring access to quality
education for underrepresented minority students.
The CAAP Program
Michigan State University offers underrepresented students a unique opportunity
to study at the institution even if they don’t meet the standard
admissions criteria. In order to be admitted those students are required
to join the College Achievement Admissions Program (CAAP). CAAP students
agree to receive academic support services from the Office of Supportive
Services during one year. Every year MSU admits almost 400 students in
CAAP. Because most of CAAP students are admitted under special circumstances
the predicted or expected GPA for them is lower than the regular students.
Study Methodology
For the purpose of our analysis we took three years of data of CAAP students:
1999, 2000, and 2001. We considered the cumulative GPA achieved during
the first semester of freshmen year and compared it with an already established
projected GPA. We also analyzed the recalculated GPA for the 2001 students.
The predicted GPA is defined by the institution and its
based on the performance of peer students during their first semester
and also take into consideration the retention rate. The recalculated
GPA is the GPA that the admissions counselors assigned after reviewing
the students coursework from ninth to eleventh grade, but taking into
consideration only academic courses (Math, Science, Social science, English
and Foreign Language. The data for the P_GPA included 1104 students. For
the R_GPA the data included 418 students.
Key findings
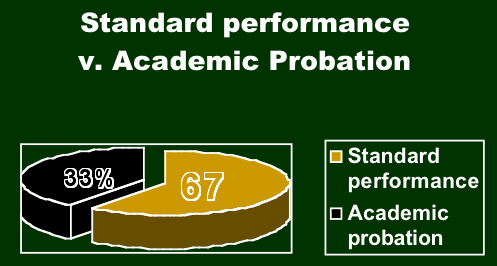
According to the Recalculated GPA for the incoming class of 2001 it was
expected that 75% of the students would have fallen in academic probation
after the first semester. The actual data shows that only 33% of the students
felt in academic probation:
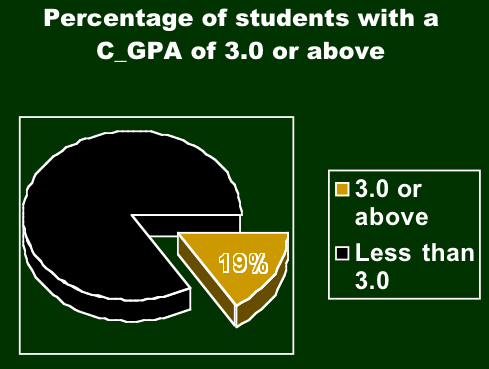
According to the Predicted GPA only one student out of 1104 (.09%) would have had a Cumulative GPA of 3.0 or above. The reality was that for the whole three years of data 19% os the students had a GPA of 3.0 or above after the first semester:
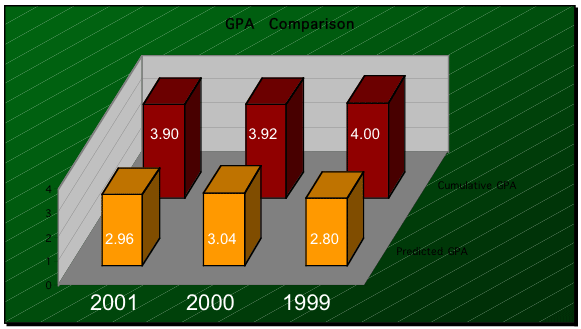
It was also found that while the highest predicted GPA
for the years 1999, 2000, and 2001 was 2.8, 3.04 and 2.96, respectively,
the highest cumulative GPA achieved for those years was 4.0, 3.92, and
3.0:
Highest Predicted GPA Vs.
Highest Cumulative GPA
Conclusions
As it was stated in the 2000-01 Report of the Consortium for Student Retention
Data Exchange, retention and graduation rates are consistently lower for
underrepresented minorities in US higher education institution. In the
other hand, the 1997 National Study of Student Support Services found
that Support Services Programs have a positive and statistically significant
impact upon students grades, credit earned and college retention.
After reviewing the available data of the MSU CAAP students we can conclude that support services do have a positive impact in MSU students. If we need to apply a Performance Based Budgeting approach to the Support Services Office, approach that required to allocate resources according to achievement of goals, objectives and outcomes (Daniel, 2001; Shulloc, 2001; Layzell, 2000), there’s no doubt that the CAAP Program should be funded for the future years.
References
Consortium for Student Retention Data Exhange.(2000-01). The retention and graduation rates report. (In http://www.occe.ou.edu/csrde).
Johnson, Sandra. (1995). Reinventing the university: managing and financing
institutions of higher education. New York: LLP Coopers & Lybrand.
Layzell T., Daniel. (2000). Linking performance to funding outcomes for
public institutions of higher education: The USexperience. In ASHE readings
in Finance in Higher Education. Pearson Custom Publishing.Boston: MA.
Massy, William. (2001). Reengineering resource allocation systems. In
ASHE readings in Finance in Higher Education. Pearson Custom Publishing.Boston:
MA.
Massy, William. (2001). Improvement strategies for administration and
support services. In ASHE readings in Finance in Higher Education. Pearson
Custom Publishing.Boston: MA.
US Department of Education.1997. National study of student support services.
(In http://www.ed.gov/offices/OPE/HEP/trio/).
Shullock, Nancy and Mernoy E Harrison. (2001). Integrating planning, assessment,
and resource allocation. In ASHE readings in Finance in Higher Education
Pearson Custom Publishing.Boston: MA.
|
||
|
Course: Budget and Finance in Higher Education (EAD 876) Term: Spring 2002 Profesor: Marylee Davis The CAAP research project gave me the opportunity to integrate the classroom experience with my work as a Graduate Assistant in the Office of Admissions and Scholarships at Michigan State University. CAAP admissions are decided by a committee in which I had the privilege of being a member. The findings of the study served as a starting point to reflect on how admissions decisions were made and to point out areas of future research. The project gave me also the opportunity to meet and present the results to the Vice-president of Students Affairs at MSU. |